Applications
TYPES OF MACHINES
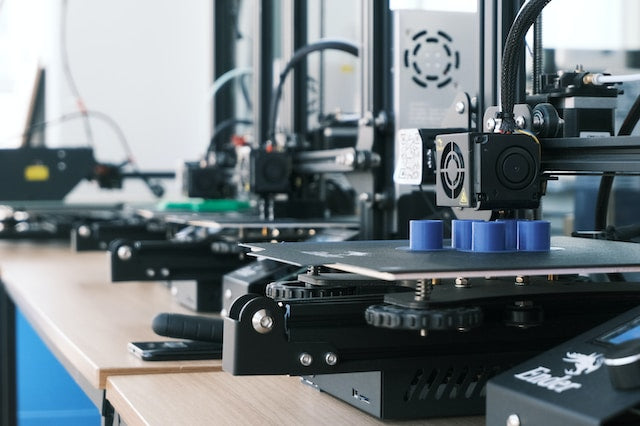

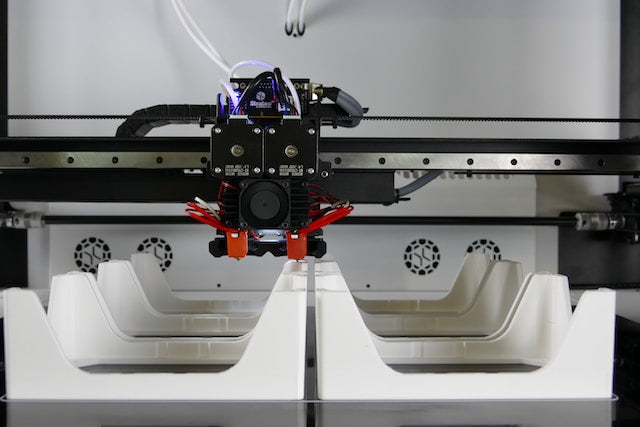
3D Printers
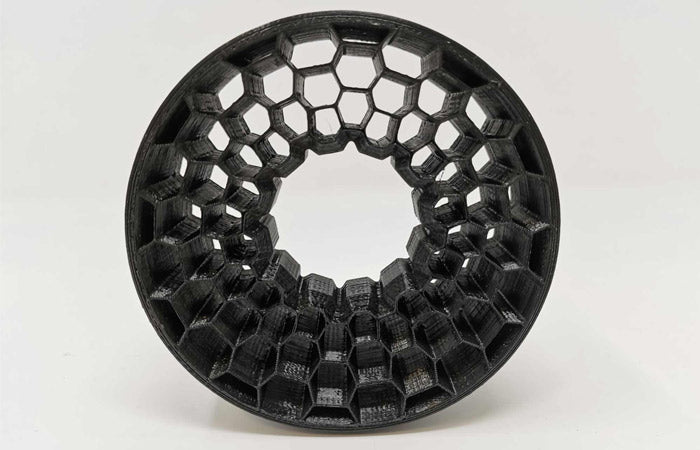
Hansford3D uses 3d printers to make its product and prototypes for customers, A 3D printer is a device that creates three-dimensional objects by adding layers of material. It uses digital designs to guide the process and can work with various materials like plastic or resin.
FDM and SLA are two common 3D printing technologies.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers melt plastic filament and deposit it layer by layer to create objects. They are affordable and versatile, but may have visible layer lines.
SLA (Stereolithography) printers use liquid resin cured by UV light to build objects with high precision and smooth surfaces. They are more expensive but excel in intricate prints.
Each technology has its strengths and is suitable for different applications.
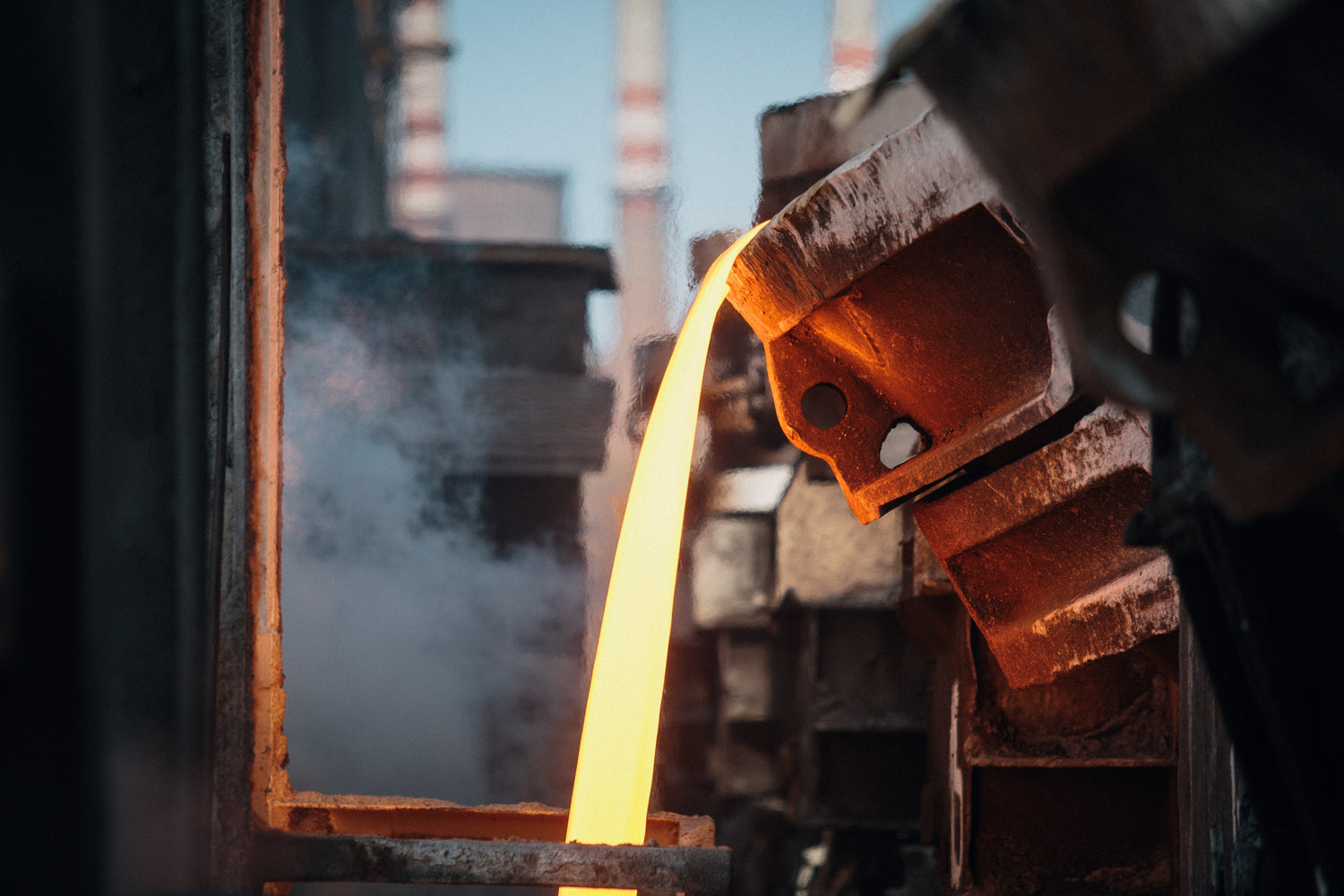

Melting Furnace Forges
A melting furnace forge is a compact device used to heat and melt metals for various purposes. It typically consists of a container, such as a crucible, capable of withstanding high temperatures, and a heat source, such as gas or electric elements. The furnace operates by generating intense heat, causing the metal inside the crucible to reach its melting point. This molten metal can then be poured into molds or used for casting, blacksmithing, or metalworking projects. Melting furnace forges are commonly used in small-scale foundries, jewelry making, and hobbyist metalworking.
TYPES OF MATERIALS

PLA
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable and renewable thermoplastic made from plant-based materials, such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is commonly used in 3D printing and packaging industries due to its eco-friendly nature and versatility.
PETG
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is a durable and transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent strength and impact resistance. It is widely used in industries such as packaging, electronics, and 3D printing. PETG offers good chemical resistance and can be easily recycled, making it a popular choice for various applications.

TPU
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a flexible and elastic thermoplastic material known for its outstanding durability and resilience. It combines the properties of rubber and plastic, offering high abrasion resistance, excellent elasticity, and good impact absorption. TPU is commonly used in applications that require flexibility and toughness, such as footwear, automotive parts, and sports equipment. It can be easily melted and molded, making it suitable for 3D printing as well.

Common and Precious Metal
Tin, aluminum, copper, silver, and gold are all metallic elements widely used in various industries. Tin is a malleable metal often used for soldering and coating other metals to prevent corrosion. Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant metal utilized in construction, transportation, and packaging industries. Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity and heat, making it vital for electrical wiring and plumbing applications. Silver is highly conductive and valued for its use in electronics, photography, and jewelry. Gold, known for its beauty and rarity, is prized in jewelry and electronics for its corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity.
CAD MODELING
-

3D Modeling
A 3D model is a digital representation of an object or scene used for visualization, design, and prototyping. It allows for detailed analysis and can be used in various industries like architecture, gaming, and manufacturing.
-

2D Drawing
A 2D drawing is a flat visual representation of an object or scene, commonly used in engineering, architecture, and design. It conveys details and measurements using lines, shapes, and symbols for communication and planning purposes.
-

Rendered Images
Rendered images are realistic digital visualizations created using rendering software. They are widely used in various industries for visualizing concepts, presenting designs, and showcasing products.



